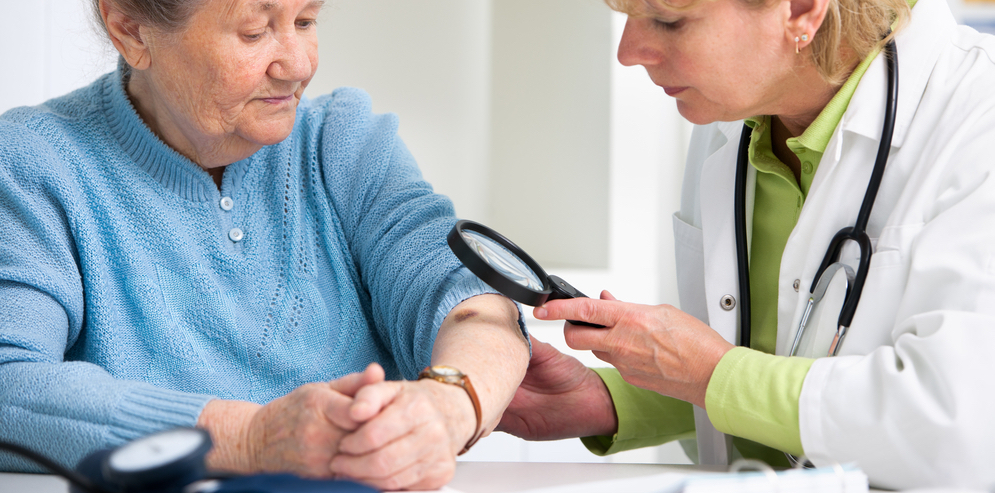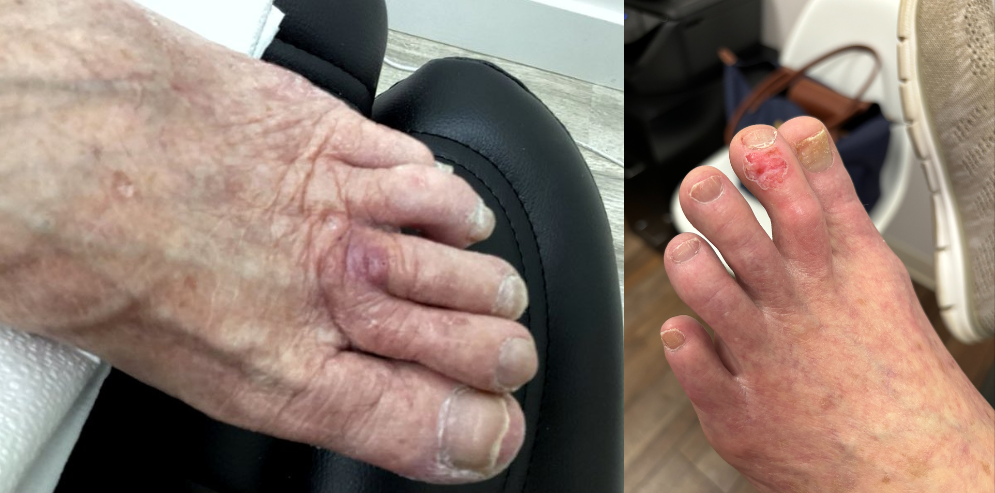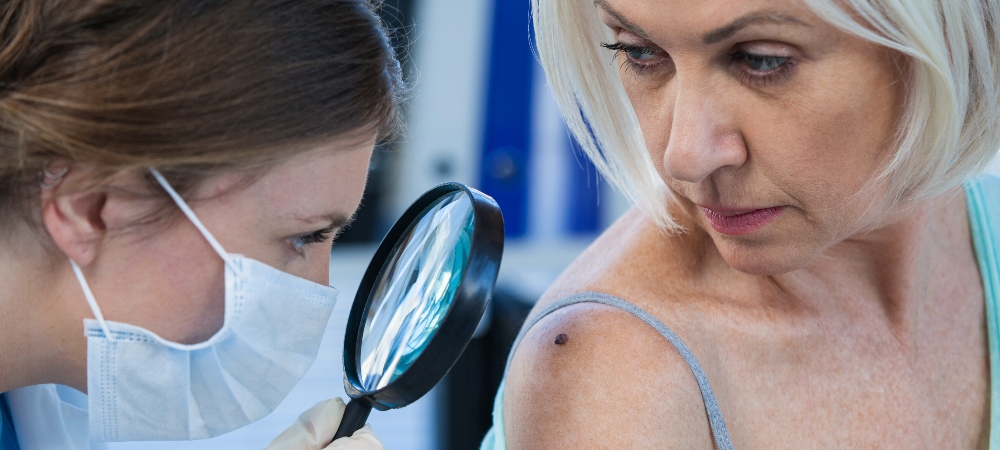
When you learn that you or someone you care about has skin cancer, it can also help to learn more about the cancer and how it’s treated. This can help you take a more active role in your care. It can also help you figure out what questions you have for your doctor.
Let’s start by talking about skin cancer. The cells in the body are always dividing and growing to make new cells that replace the older cells. Cancer happens when cells in the body change and start to grow out of control. This change can happen for many reasons. One of them is being exposed to too much UV radiation. We are exposed to this type of radiation when we are in the sun, use tanning beds, or at some types of jobs like welding. The more you are exposed to UV rays, the more likely it is that they will change the way your skin cells grow and divide.
If Radiation Can Cause Skin Cancer, How Can it Also Be Used to Treat and Cure it?
The same way radiation causes changes to healthy cells, it can also be used to cause changes in the cancer cells. Instead of causing the cells to grow, it can be used to cause the cancer cells to die.
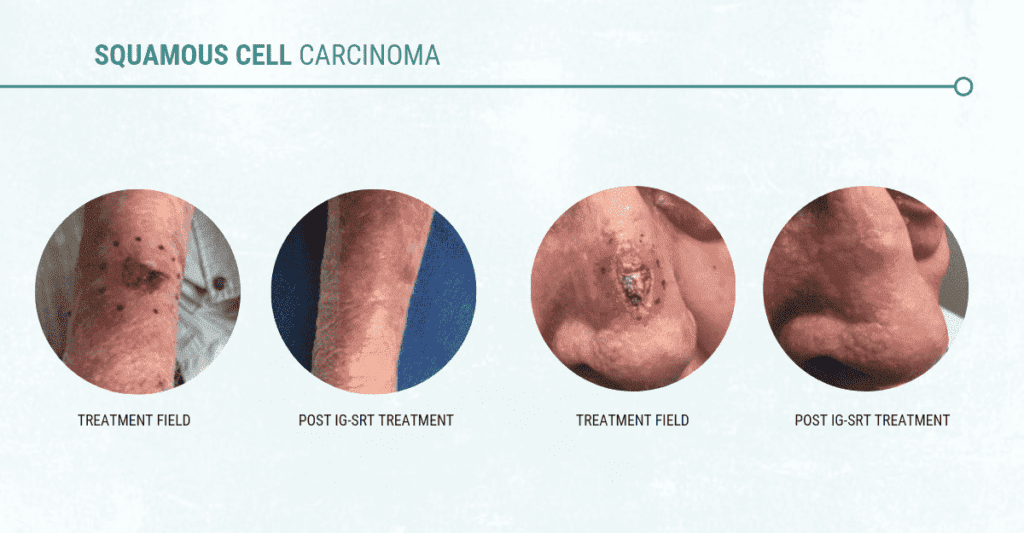
Image-Guided SRT is a type of skin cancer treatment that uses very low levels of radiation to kill cancer cells. This is the same type of X-ray energy that dentists use. Image-Guided SRT starts with an ultrasound to measure how big and deep the cancer is. That tells the doctor exactly how much X-ray energy is needed. That energy is given only to the skin cancer, leaving the healthy skin untouched. For most people, after three to five treatments per week for several weeks, the cancer cells die and the cancer is cured. There is no cutting, bleeding, or surgical scars and no reconstructive surgery is needed.
Image-Guided SRT is done right in the dermatologist’s office and can cure basal and squamous cell skin cancers. If you or someone you know have one of these common types of skin cancer and do not want to have surgery, ask your dermatologist about Image-Guided SRT.