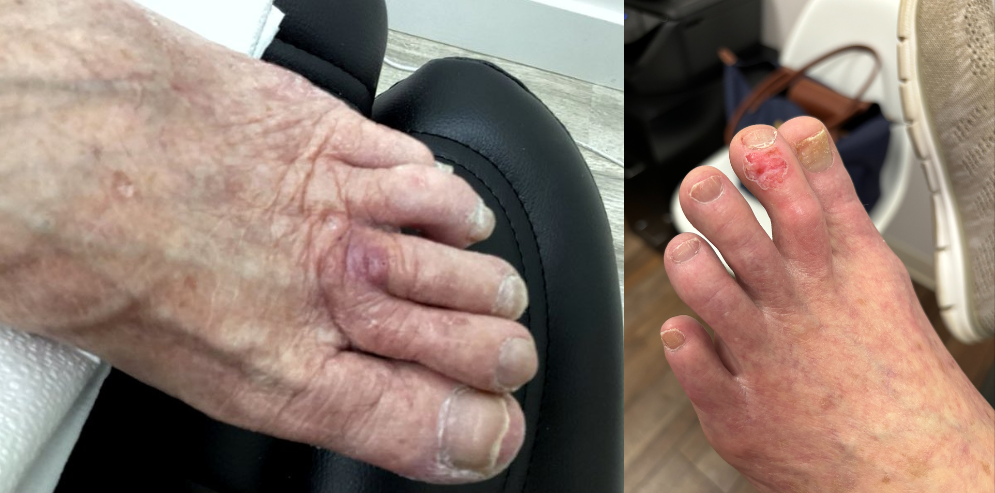
Some people worry that the radiation used to treat skin cancer can actually cause cancer. This concern is common when people who have had one skin cancer get diagnosed with another. The new cancer is often mistaken for the old cancer coming back. While it is true that radiation causes skin cancer, the new cancer was most likely caused by radiation from the sun’s rays or tanning beds—not the radiation from treatment.
How Does Radiation for Skin Cancer Work
Radiation therapy, or radiotherapy, is often implemented when a skin cancer area is large or is located on a part of the body where surgery would be difficult. Some people with skin cancer can’t have surgery for one reason or another, and radiation therapy is a viable option. Radiation is focused on the skin cancer area. A beam of low-energy x-rays (superficial radiation therapy) or electrons (electron beam radiation) is aimed directly at the skin cancer and begins to damage and kill the cancer cells. Great care is taken to avoid hitting normal cells with radiation, but if it happens, the cells will more than likely repair themselves.
Treatment with Radiation Does NOT Cause More Skin Cancer
Radiation is a common treatment for skin cancer. Depending on the type of skin cancer radiation treatment, radiation can be a very effective cure. In fact, Image-Guided Superficial Radiation Therapy (Image-Guided SRT) has been shown to cure over 99% of basal and squamous cell skin cancers.
It is important to remember that up to half of all people who have had one skin cancer will have another within 5 years. If you had radiation for skin cancer in the past and have another skin cancer in the same area, it is likely caused by exposure to the sun’s damaging rays.
Why Does Radiation Kill Cancer Cells?
Radiation damages the DNA of skin cancer cells. The goal is to damage the DNA of the cancer cells to a point where they can’t regenerate; they stop dividing or die. Radiation causes single strand breaks (SSB) and double strand breaks (DSB) within the cells. When the cancer cells die, they’re broken down and removed from the body. Radiation therapy takes days or weeks before the DNA of the cancer cells is damaged enough for them to begin dying. After radiation therapy ends, cancer cells continue to die for weeks or months.
The Danger of Ultraviolet Radiation
Radiation from the sun’s rays and tanning beds is the leading cause of skin cancer. More specifically, it is the ultraviolet (UV) radiation that causes skin cancer. The best way to avoid UV radiation and prevent skin cancer is to use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a skin protection factor (SPF) of 15 or higher, and to avoid using tanning beds and sun lamps.
Why Does Radiation from UV Rays Cause Cancer?
Radiation has high-energy photons that cause breaks in DNA strands in normal cells (as well as cancer cells). Non-cancerous cells can repair themselves to a certain degree, but they don’t always return to normal; the damage can cause defects. A break in a DNA strand that contains a tumor-suppressing gene can result in the development of cancer.
The good news is that cancer cells are more susceptible to radiation than normal cells. When radiation breaks the DNA strands within a cancer cell through radiation therapy, it essentially turns off their ability to divide rapidly.
How to Stay Ahead of Skin Cancer
The most effective way to stay a step ahead of skin cancer is to get a full-body skin check each year and to use a broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 15 or higher). Make your skin health a priority and talk with your dermatologist about any suspicious spots you notice. Together, you can work to find and treat any skin cancers early, before they become too serious. If you’ve been diagnosed with basal cell or squamous cell skin cancer, and are considering radiation therapy as treatment, contact us online or by phone to find an Image-Guided SRT provider in your area.