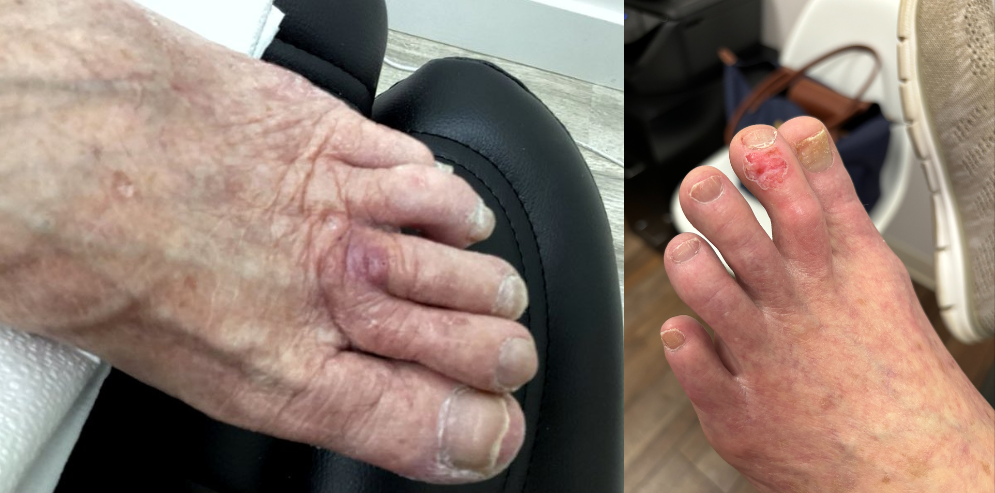
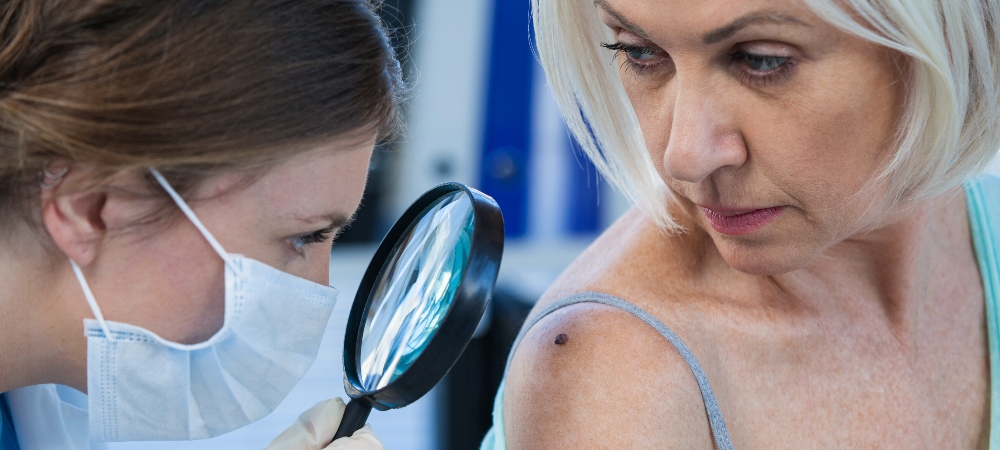
There is a clear, proven link between excessive sun exposure and skin cancer, but how does the sun cause skin cancer? The sun’s radiation damages your cells, and visible effects like tanning and sunburn are clear signs of this damage. If the damage is significant enough, your skin cells may start to reproduce too quickly and grow out of control. We’ll take a closer look at the process below.
Skin Cancer from Sun Exposure: How it Happens
Here’s how you can get skin cancer from sun exposure:
- The sun’s light contains several types of UV radiation. Two types of this radiation—UVA and UVB—reach the earth’s surface.
- UVB rays cause sunburns, while UVA rays cause accelerated skin aging. Although UVB rays have a greater impact on the likelihood of skin cancer both types of radiation contribute to skin cancer formation.
- Essentially, both types of UV radiation penetrate your cells and cause damage to their DNA. This damage is replicated with the cell’s reproduction, and it is cumulative.
- If your cells accumulate too much DNA damage from this radiation, they may start growing and reproducing too rapidly.
- The out-of-control growth that develops is known as skin cancer.
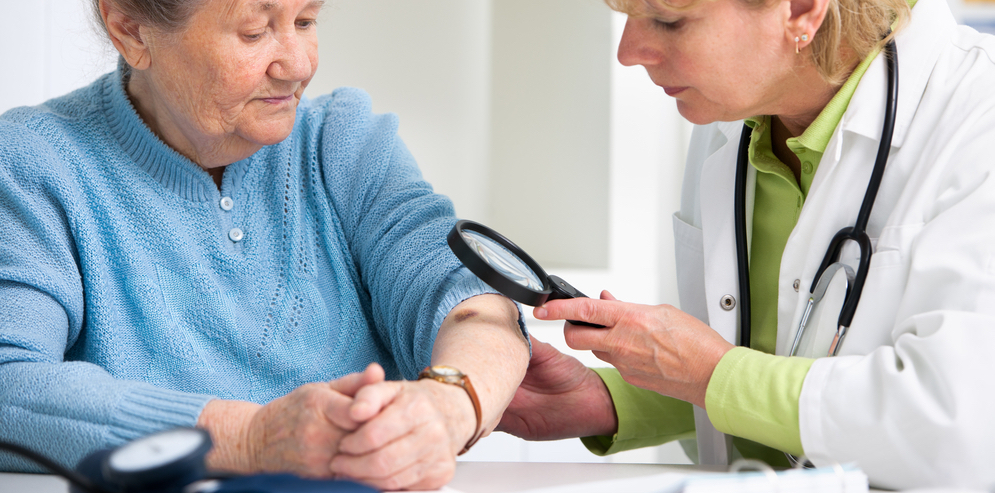
Although the likelihood of metastasis varies depending on the type of skin cancer in question, most skin cancers can eventually spread from the skin to other organs. This is why early detection is so important.
UV Radiation and Skin Cancer: Facts and Statistics
- How many sunburns cause skin cancer? There is no definitive threshold, but statistics show that having five or more sunburns double your risk of developing a melanoma.
- Even one blistering sunburn in childhood or adolescence significantly increases your risk of developing skin cancer later in life.
- Studies show that up to 86% of melanoma skin cancers are attributable to the UV radiation that is emitted by the sun.
- Additionally, roughly 90% of common skin cancers are correlated with UV radiation from the sun.
- Those who use sunscreen every day lower their risk of squamous cell skin cancer by roughly 40%.
- Indoor tanning devices are not a safe alternative. These beds emit UV radiation at a rate of up to 10 to 15 times higher than the sun.
Regularly using strong, broad spectrum SPF sunscreen is one of the most effective ways to lower your likelihood of skin cancer. UV radiation even reaches the earth on colder, cloudier days—and not just in the summer.
For Common Skin Cancer, Consider Image-Guided SRT
If you receive a common skin cancer diagnosis, ask your doctor if Image-Guided SRT (utilized by GentleCure™) is right for you. This type of treatment uses targeted radiation to attack skin cancer cells before they can spread, without the risk of surgical scarring that comes with Mohs surgery. Find out how it works today.