The most common places to get skin cancer are those areas that regularly see high levels of ultraviolet light exposure, including the scalp, face, nose, and ears—but skin cancer can appear in other less exposed areas, especially if you have highly pigmented skin. This is true for melanoma, as well as for basal cell skin cancer and squamous cell skin cancer.
8 of the Most Common Areas to Get Skin Cancer
Ultimately, skin cancer can appear anywhere on the body. It’s important to perform regular, full-body inspections and see a dermatologist if you notice any worrisome, unexplained changes. With that said, keeping a close watch on the body areas most susceptible to skin cancer can only help you in the long run. Here’s where you should focus your investigation:
- Face – Day in and day out, your face is one of the most exposed parts of your body. In fact, up to 85% of skin cancer spots develop on the patient’s face, or on one of several nearby areas.
- Scalp– Hair and hats can obscure the scalp, protecting it from excess sun exposure. But in people who are balding or who have lighter, thinner hair, skin cancer on the scalp can be a serious risk. You can check your own scalp with a mirror, but you should also ask your barber or hairdresser to keep an eye out for you.
- Ears – Do you regularly put sunscreen on your ears? You should! The ears are the third most common place to get skin cancers like basal cell skin cancer, and other more dangerous types of skin cancer can appear there as well.
- Lips – Technically, the lips are part of the face, but this area deserves special attention because the skin here is much thinner than it is on other parts of the body. People are also relatively unlikely to protect their lips with sunscreen.
- Neck – Alongside the face, the neck accounts for a significant portion of skin cancer spots. It’s the third most common place to find melanoma, and skin cancers like basal cell skin cancer and squamous cell skin cancer are even more common here. It’s a good idea to protect this area with the same sun protection that you use for your face.
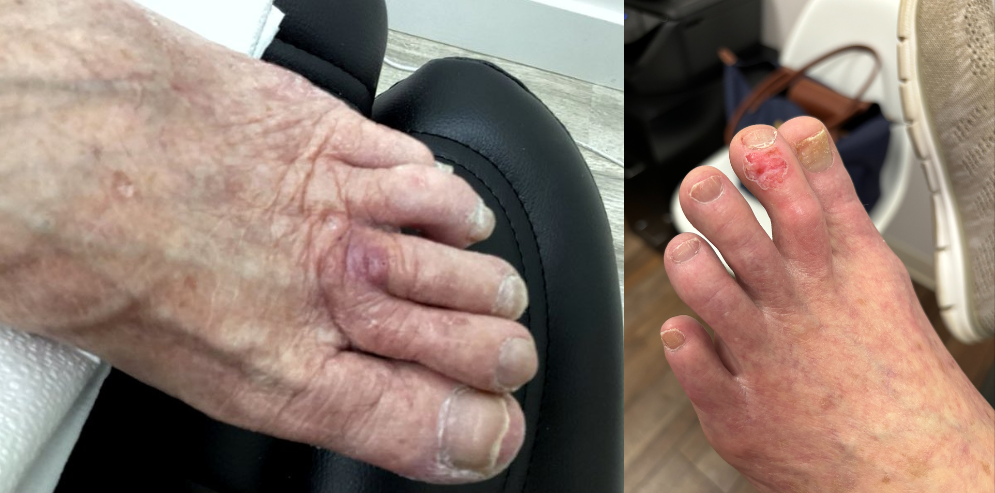
- Hands – At least in people with low skin pigmentation, skin cancer that appears on your hands is most likely to be squamous cell skin cancer, which is relatively slow-growing. However, the palms of the hands and the nail beds are two of the most common areas to get skin cancer (specifically melanoma) in people with darker skin tones. The same goes for the soles of the feet.
- Chest & Back – These areas can be exposed to a great deal of sunlight over the course of a person’s life. It’s also worth noting that this area is one of the most common places to encounter melanoma in men.
- Legs – In women especially, the legs are a common place to encounter skin cancer. The lower legs and ankles deserve extra attention, as these areas are the most likely to see the sun.
Once again, it’s important to note that skin cancer can appear anywhere. Although you should be aware of the areas where skin cancer is most likely to turn up, there’s no substitute for comprehensive screenings.
Examining the Body Areas Most Susceptible to Skin Cancer
Now you know where to look, but what, exactly, should you look for? Skin cancers can vary in appearance, and even though melanoma is the most recognizable and the most deadly form of skin cancer, it isn’t the most common. Be on the lookout for all of the following:
- Basal cell skin cancer most commonly appears as a small translucent raised bump. It tends to look brown or glossy black in people with darker skin tones, or shiny and pearlescent in people with less skin pigmentation. It could also look like a flat scaly patch or a lesion that looks waxy, brown, black or blue. Once more, it most commonly appears on the head and neck.
- Squamous cell skin cancer often takes the form of a scaly red patch, but it might also look like an open sore or a growth with a central depression. With this form of skin cancer, the skin is often rough and cracked. It is common to find squamous cell skin cancer on the face, the neck, and the backs of the hands.
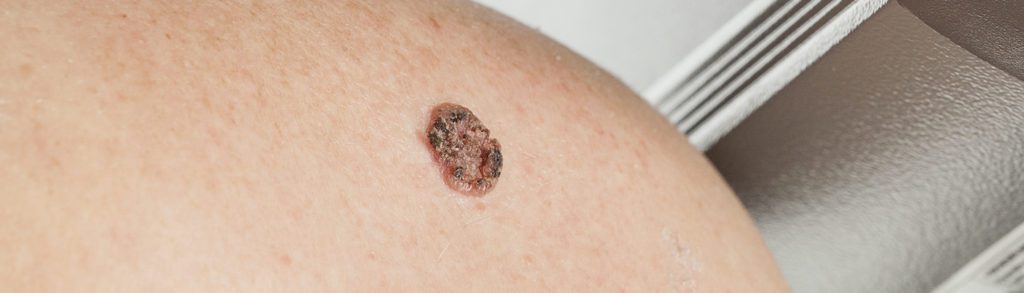
- Melanoma skin cancers often look like moles—at least at first. Early detection is especially important here, so be on the lookout for moles that are asymmetrical, have uneven borders, vary in color, are more than 6 mm in diameter, or are evolving, i.e. changing in size or shape. Remember ABCDE when you’re performing your inspections.
Next Steps
Annually, some 9,500 people across the U.S. are diagnosed every day with skin cancer. One out of every five people will experience skin cancer by the age of 70. Here at GentleCure, we’re passionate about providing you with information on skin cancer prevention, detection, and treatment. The typical treatment for most common skin cancers is surgery, which may be painful, leave a scar and limit daily activity. Advancements in technology mean there is now a surgery-free approach to skin cancer treatment with effective results.
If you’ve been diagnosed with basal cell or squamous cell skin cancer, please contact a Skin Cancer Information Specialist at 855-936-4411 for more information or visit our IG-SRT locations page to find a dermatologist that offers GentleCure.